
Fannyann Viola Eddy

WHRDs are self-identified women and lesbian, bisexual, transgender, queer and intersex (LBTQI) people and others who defend rights and are subject to gender-specific risks and threats due to their human rights work and/or as a direct consequence of their gender identity or sexual orientation.
WHRDs are subject to systematic violence and discrimination due to their identities and unyielding struggles for rights, equality and justice.
The WHRD Program collaborates with international and regional partners as well as the AWID membership to raise awareness about these risks and threats, advocate for feminist and holistic measures of protection and safety, and actively promote a culture of self-care and collective well being in our movements.
WHRDs are exposed to the same types of risks that all other defenders who defend human rights, communities, and the environment face. However, they are also exposed to gender-based violence and gender-specific risks because they challenge existing gender norms within their communities and societies.
We work collaboratively with international and regional networks and our membership
We aim to contribute to a safer world for WHRDs, their families and communities. We believe that action for rights and justice should not put WHRDs at risk; it should be appreciated and celebrated.
Promoting collaboration and coordination among human rights and women’s rights organizations at the international level to strengthen responses concerning safety and wellbeing of WHRDs.
Supporting regional networks of WHRDs and their organizations, such as the Mesoamerican Initiative for WHRDs and the WHRD Middle East and North Africa Coalition, in promoting and strengthening collective action for protection - emphasizing the establishment of solidarity and protection networks, the promotion of self-care, and advocacy and mobilization for the safety of WHRDs;
Increasing the visibility and recognition of WHRDs and their struggles, as well as the risks that they encounter by documenting the attacks that they face, and researching, producing, and disseminating information on their struggles, strategies, and challenges:
Mobilizing urgent responses of international solidarity for WHRDs at risk through our international and regional networks, and our active membership.
Our women ancestors form a circle
Sacred, alive, powerful
We are in the middle
Feeling their strength.
The drum beats a sound of earth
Our skin dresses in colours
We are green, red, orange, blue, violet, black
The drum beats a sound of earth
A voice vibrates, a scream emanates, a song rings out, lulling to sleep, awakening consciousness.
The drum beats a sound of earth
A gaze of complicity, friendship profound.
The drum beats a sound of earth
Ours is but one heart, beating a rhythm of the soul, inviting us to move, inspiring desire, and showing us a path.
One of communal togetherness, power of the people, self-government, a women’s revolution of subversive communal care.
The drum beats a sound of earth
And I invite you to join, to be voice, skin, gaze, seed, fire, song, communion.
The drum beats a sound of earth
And I invite you to discover it, to love it, to know it, and to defend it from the heart of the community
For 25 years they have lived along the same dusty streets, at the top of a hill named after a lion. They come from different places, many from traditional farming communities. Their skin is the colour of rebellion, the colour of a cardon cactus, because in them lives the spirit of the semi-arid Lara State, which is where their love for life comes from, their appreciation, care and protection of water and land. They are heiresses of the Gayon and Ayaman lineages, Indigenous communities that lived and live in the northern part of Lara State.
From the time they were very young they learned that maternity is a role from which it is not easy to escape. Caring for children, home and husband, washing, ironing, cooking, cleaning—everything had to be impeccable, people insisted.
And that was life—that and violence, insults, abuse, hitting, scheming, complaints were to be expected. It seemed almost natural, and that is how they spent their days. Everyday life on those dirt streets living in little houses of tin sheet metal without any electricity or running water. That was poverty, the precarity of when a man would arrive, yes, a man, a project. And then, an unusual revolution because it came about without war.
Then they were invited to go out, they were invited to take to the streets and occupy public space. In the process, the women tore down doors and windows, broke chains, let their hair down and they felt free, free like runaway slaves, Caribbean rebels, freedom fighters.
And those concepts of independence and sovereignty are something that those who had the chance to study had read about, but feeling it, feeling like the protagonists of a process of social transformation—that is an important victory that we have to mention and we cannot forget.
At the top of that hill one can feel the complicity, the shared fire, the years of struggle. They tell of how one of them would go around with her parasol in the afternoons from house to house having coffee and conversing with the people she would invite, convincing them
We are going to make a community council!
Let’s move forward together as a community!
Let’s make plans for education, sports, health, nutrition, a women and gender equality committee, the economy.
We can form our own People’s Government so our Neighbourhood can Be Beautiful!
And that is how the houses came, the doctor’s office, daycare, electricity, potable water. These are some of the community’s achievements, some of our common dreams come true.
And you might ask how a cuentera, a storyteller, made her way to a hill with the name of a lion
And I will tell you: it’s that I was born rowdy, always fighting, I was born a wanderer my grandmother would say, born ready Comandante Chavez would add, from so much walking, grumbling, fighting, and doubting that military man, that I would end up becoming convinced by the community project, by the idea of self-government, of the people managing their own resources, of all the power going to the communities, and so I was convinced.
But I knew something was missing because the women, the women of the community kept building up the people’s power and putting our hearts in the anti-imperialist and anti-capitalist fight, but there is something that hurts and continues to affect us. There are wounds from a patriarchy still present.
So one day, I found myself crying and the drum of the earth beat and our women ancestors spoke.
I found myself surrounded by a group of women who held me up, who contained me as I spilled over in front of them, as it both hurt and liberated me at the same time. That is how I discovered that love among women heals you, saves you, and that our friendship is profoundly political and that sisterhood is a way of being, of living life. From that moment on I never felt alone again, I never felt like an island again, because I know there is a group of women who carry me, bring me, love me, care for me and me for them. I know that this way of becoming a feminist with the mysticism of women loving life is an experience of feeling connected and loved by women, even if you never see them again. How not to want this that happened to me, to happen also to other women, this new beginning, this birth of a new heart is a gift from the goddesses that must be shared.
So I decided to join the women and I began walking from community to community to learn about others’ experiences. We began debating health, education, nutrition, we began preaching the anti-patriarchal word and calling for communities free of machismo. We insisted on recovering ancestral knowledge, intuition, we decided to defend life by talking about abortion and we found ourselves laughing, crying, debating, reflecting. I find myself with Macu, with the China, Yenni, Carolina, Maria, Ramona, Irma, and even with our sister Yenifer who left us not long ago.
This is my homage to them, the women of the hill, the lioness women, the ones who without a doubt have sown a seed in me with so much force it now beats with my heart.
Without a doubt they blaze a path, they are the ones who make caring for a family possible, collective care. They are also a force, a force in a territory that fights to overcome the embargo, the patriarchal violence, the political treason, to overcome the bureaucracy and the corruption.
Without a doubt they blaze a path
Without a doubt they are a compass
Without a doubt they are the heart of the community
Thank you.
por Amal Amer
Rezo con mi familia por primera vez en seis años envueltx en un keffiyah que recogí de un contenedor de basura. (...)
arte: «Angels go out at night too» [Los ángeles también salen de noche], Chloé Luu >
✉️ Sur invitation uniquement
📅 Mardi 11 mars 2025
🕒 14.00h-16.00h EST
🏢 Chef's Kitchen Loft with Terrace, 216 East 45th St 13th Floor New York
Organisé par : Consortium de l’Observatoire sur l'universalité des droits (OURs)


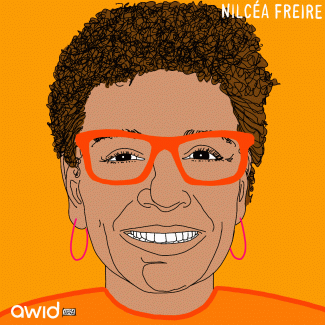
Nilcéa Freire was a Brazilian feminist activist, politician and academic. A persevering advocate for women’s rights and those of underrepresented minorities in the country, her life and work carried a long history of struggles and victories.
"While resisting we have to keep pushing for progress, and what we can achieve at this time, in my view, will be through the stupendous organization of young white women, and especially black women, in all of the state capitals and large cities of Brazil." - Nilcéa Freire
In 1999 she became the first woman to occupy the position of Dean at the State University of Rio de Janeiro. Here, she spearheaded the implementation of the first affirmative action policy for students graduating from public schools, requiring reserved places specifically for low-income black students in a public university. This system was adopted in dozens of other public universities.
Some years later, Nilcéa headed the Special Secretariat of Policies for Women in the government of former president Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva. In this capacity, she led the first National Women’s Conference. Over 12,000 women from across the country participated and the result of this collective work was embodied in the National Plan for Policies for Women.
Her commitment to women, Afro-Brazilians and indigenous peoples was also strongly reflected in her work to promote their rights through initiatives of the Brazil Ford Foundation office where she was a regional director.
The feminist activist Manoela Miklos recounted Nilcéa to be "a woman without equal".
At the age of 66, Nilcéa passed away in Rio de Janeiro on 29 December 2019 of cancer.
"Without words for the news of the death of dear Nilcea Freire. It is too sad to know that she left so early. She was always part of the ranks of those who do not settle for the injustices of the world. She was the Minister of Women, an activist, always active in the feminist cause. Much missed!” - Jandira Feghali, Federal Deputy
Watch Brazilian feminist Nilcea Freire on why we need to show solidarity with Brazil
Por Marianne Mesfin Asfaw

Tengo muchos recuerdos queridos de mi recorridofeminista, pero hay uno en particular que se destaca. Fue durante mi época en la escuela de posgrado, una conferencia a la que asistí como parte de un curso de Teoría Feminista. La conferencia trataba sobre feminismo africano y, en ella, la profesora habló de la historia del panafricanismo, de su carácter patriarcal, centrado en los hombres, y de cómo los estudiosos panafricanistas perpetuaban el borramiento de las mujeres africanas. La conferencista señaló que las contribuciones de las mujeres africanas a las luchas anticoloniales y descoloniales en el continente rara vez, o nunca, se analizany no se les da el debido crédito. Leímos acerca de las académicas feministas africanas que desafían ese borramiento y dan a conocer activamente las historias de los movimientos y los esfuerzos de resistencia liderados por mujeres africanas. Parecetan sencillo, pero lo que más me llamó la atención fue que alguien juntara las palabras africana y feminista. Mejor aún: descubrir que había muchas más de nosotras ahí afuera, luchando contra las complicaciones de la historia, la política y las normas sociales en distintos rincones del continente, y que todas estábamos utilizando una perspectiva feminista para hacerlo. Salí de esa conferencia conmovida y completamente alucinada. res de mis amigas (todas feministas africanas) y yo nos quedamos un rato comentando fuera del aula. Todas estábamos impresionadas por la genialidad de la conferencia y su contenido pero, sobre todo, sentimos que estábamos siendo tenidas en cuenta. Ese sentimiento fue el que más me llamó la atención.
Enamorarse del feminismo fue electrizante. Fue como sentir que por fin puedes hablar con la persona que te gusta desde hace mucho tiempo y descubres que también le gustas. Lo llamo mi enamoramiento porque durante la escuela secundaria me consideraba feminista pero sentía que no sabía lo suficiente sobre el tema. ¿Había una forma correcta de ser feminista? ¿Y si no lo estaba haciendo bien? Cuando asistí a mi primera conferencia de Estudios de las Mujeres obtuve respuestas para algunas de estas preguntas. Fue emocionante conocer historias de resistencia feminista y de desmantelamiento del patriarcado. Me sentí muy afirmada y validada, pero también sentí que algo me faltaba.
Profundizar mi relación con el feminismo a través de la academia en una institución en la que el estudiantado y el personal docente eran en su mayoría blancx, significó que, durante esos primeros años, me diera cuenta de que rara vez hablábamos sobre cómo la raza y la antinegritud se ponen en juego en los movimientos feministas hegemónicos. En la mayoría de las asignaturas teníamos tal vez una semana, o peor aún, una clase, dedicada a la raza donde por lo general leíamos algo de bell hooks, el trabajo de Kimberly Crenshaw sobre interseccionalidad, y tal vez, a Patricia Hill Collins. A la semana siguiente volvíamos a dejar de lado el tema. Lidié con todo esto dándole un lugar central a la raza y al feminismo negro en casi todas mis tareas, escribiendo sobre el pelo negro y las políticas de respetabilidad, la hipersexualización de los cuerpos de las mujeres negras, y mucho más. Con el tiempo me di cuenta de que intentaba llenar un vacío, pero no sabía muy bien cuál era.
El momento en que el círculo se cerró de manera perfecta fue cuando descubrí que había un feminismo africano y lo estudié. Me di cuenta de que teníamucho más por aprender, principalmente que mi africanidad y mi práctica feminista no tenían por qué estar separadas. Al contrario: tenían mucho que aprender la una de la otra, y había feministas africanas que ya estaban haciendo este trabajo. Esa era la pieza que faltaba y que me fue tan esquiva durante mi exploración del feminismo a lo largo de mi carrera académica.
Para mí, el feminismo es la antítesis de la apatía social y política. También significa que una vez que adoptas una perspectiva feminista, nada puede ser igual. Con mis amigas solíamos decir que era como ponerse unos anteojos que nunca te puedes quitar porque ahora ves el mundo tal y como es, con todos sus desastres. Desastres que no puedes ignorar ni dejar de lado. Es por eso que mi compromiso con el movimiento feminista es no dejar nunca de aprender, seguir ampliando el alcance de mi empatía y no vivir nunca de forma pasiva. Dedicar más tiempo y espacio en mi vida a los movimientos feministas, y seguir amplificando, celebrando, documentando y citando el trabajo de las feministas africanas. También me comprometo a darle un lugar central al cuidado y a dar prioridad al placer en este recorrido feminista porque no podemos sostener nuestros movimientos sin esto.
par Fatima B. Derby
En 2017, la campagne #ManifestezVotreSolidarité a mis en évidence la manière dont les jeunes féministes pouvaient construire un avenir féministe en étant là les unes pour les autres, en participant à des conversations transrégionales, en marchant en solidarité avec d'autres activistes et en collaborant entre les mouvements. (...)
< illustration : « Laisse-les pousser », par Gucora Andu
This story is about how an increasingly diverse group of feminists from the Pacific organized through the years to attend the AWID Forums and how that process changed them personally, as organizations, and as a movement through what they learned, discovered and experienced. It illustrates the importance of the Forums as a space through which a region that tends to be marginalized or ignored at the global level can build a strong presence in the feminist movement that is then replicated at other international women’s rights spaces.

Leah Tumbalang fue una mujer lumad de Mindanao, en Filipinas. La historia del pueblo indígena lumad abarca generaciones de resistencia contra la minería corporativa a gran escala, de protección de los territorios ancestrales, los recursos y la cultura, y de lucha por la autodeterminación.
Leah era una líder lumad, y dirigente de Kaugalingong Sistema Igpasasindog to Lumadnong Ogpaan (Kasilo), una organización lumad y campesina que lucha contra la instalación de corporaciones mineras en Bukidnon, en la provincia de Mindanao. Fue inclaudicable en su activismo anti minería, al emprender con fervor campañas contra los efectos devastadores de la extracción de minerales en el medio ambiente y las tierras de los pueblos indígenas. Era también una organizadora política de la lista electoral Bayan Muna, que integra el partido político de izquierda Makabayan.
Durante casi una década Leah (junto con otrxs integrantes de Kasilo) recibió amenazas debido a su oposición al despliegue de grupos paramilitares, que se cree son respaldados por intereses mineros.
«Como líder lumad de su comunidad, ella está en la primera línea de lucha por sus derechos a la tierra ancestral y a la autodeterminación.» - Kalumbay Regional Lumad Organization
Estar en la vanguardia de la resistencia también significa, a menudo, ser un blanco para la violencia y la impunidad, y Leah no solamente recibió numerosas amenazas de muerte, sino que fue asesinada el 23 de agosto de 2019 en la ciudad de Valencia, en Bukidnon.
Según un informe de Global Witness, «en números absolutos, Filipinas fue el país peor afectado» en lo que respecta a activistas ambientalistas asesinadxs en 2018.
Lee el informe de Global Witness, publicado en julio de 2019

« J’ai subi des violences sexuelles, des blessures physiques et d’autres formes de violence lorsque je manifestais sur les lignes de front. Mais je ne m’arrêterai jamais, tant et aussi longtemps que nous n’aurons pas de régime civil au Soudan. Nous devons arrêter la militarisation de l’État. Nos corps ne doivent plus être traités comme des champs de bataille »
déclarait Amal*, une manifestante de 23 ans**
Les femmes sont à la tête de la révolution au Soudan depuis quatre ans. Leur leadership ne s’est pas limité à la rue : elles étaient la force motrice de la résistance continue à tous les niveaux. Les femmes et les jeunes féministes sont devenues la conscience alerte du mouvement pour le changement et la démocratisation au Soudan. Dès la première manifestation contre l’ancien régime dans la ville d’Aldmazein, dans la région en conflit du Nil Bleu, le 13 décembre 2018, de jeunes écolières sont devenues les porte-voix réclamant la fin de 30 années de dictature militaire et de Frères musulmans.

Le mouvement féministe mené par de jeunes femmes âgées de 16 à 35 ans a créé une révolution au sein de la révolution incessante depuis quatre ans au Soudan. Les voix des jeunes femmes qui occupent l’espace dans les rues, sur les réseaux sociaux, au sein de la société civile et des organisations politiques sont suffisamment fortes pour avoir remodelé l’opinion publique et questionné les normes sociales. Les discussions sur les violences sexuelles et basées sur le genre et les tabous de la violence domestique et des processus décisionnels dominés par les hommes sont devenues des débats courants pour la première fois dans l’histoire du Soudan. Les équipes de football féminines, les femmes porte-parole de comités de la résistance et les syndicats professionnels dirigés par des femmes sont quelques-uns des faits saillants de la nouvelle vague du mouvement féministe au Soudan. Des jeunes femmes se définissant fièrement et publiquement comme féministes est le gain le plus important, dans un pays dirigé depuis trois décennies par un islam fondamentaliste. De jeunes hommes soutenant l’activisme féministe et s’identifiant eux-mêmes comme féministes est un autre progrès qu’il convient de souligner.
Ce progrès n’est pas sans coût, tout comme il n’est pas parfait. Les activistes féministes, les groupes et les activistes se retrouvent face aux difficultés typiques rencontrées dans les contextes conservateurs et affectés par des conflits. Mais l’impact du mouvement des jeunes féministes au Soudan mérite d’être encensé. Dépasser les obstacles internes des différences de culture, de religion et des conflits historiques est un défi en soi, que les jeunes féministes au Soudan semblent relever activement. La création d’écoles féministes au Darfour et dans le Kordofan révèle la trajectoire unique du travail des jeunes féministes au Soudan, dont nous pouvons tirer des enseignements.
Il n’est pas possible de nommer les jeunes femmes à la tête de ces efforts et les groupes de femmes actives sur le terrain, du fait des nombreuses préoccupations sécuritaires suite au coup d’État militaire toujours en cours. Mais leur résilience, leur force et leur courage devront figurer dans les livres d’histoire. Ces jeunes femmes audacieuses à la tête de la résistance dans les rues, derrière leurs écrans, dans différentes professions et sur différents terrains d’activisme façonnent l’avenir du Soudan. Les jeunes féministes au Soudan créent de nouveaux espaces pour que des récits et des discours féministes restructurent la distribution du pouvoir, dans ses aspects politiques, économiques et sociaux.
Malgré l’immensité de la violence, la résurgence d’un islam fondamentaliste, la militarisation et la réduction des espaces civiques, les activistes féministes au Soudan restent ancrées dans leurs sororités. Elles demeurent une incroyable source d’inspiration pour les mouvements féministes à travers le monde.
Nazik Awad
* Amal est un pseudonyme afin de protéger la jeune activiste citée.
** Le Soudan vit une révolution constante depuis 2018. Une nouvelle vague a démarré après le coup d’État militaire du 25 octobre 2021.
by Haddy Jatou Gassama
The Mandinka tribe of The Gambia has a custom of measuring the first wrapa used to carry a newborn baby on its mother's back. (...)
artwork: “Sacred Puta” by Pia Love >
A Critical Dialogue on Gender Equality and Human Rights
✉️ Online registration available. Register here
📅 Friday, March 21, 2025
🕒 2.30pm EST
🏢 Church Center of the United Nations, 11th Floor. 777 United Nations Plaza, New York, NY 10017
🎙️AWID speaker: Anissa Daboussi, Manager, Advancing Universal Rights and Justice team
Organizer: IWRAW AP, OURs, AWID, SRI
The AWID Forum is the world’s largest event that wholeheartedly centers feminist and gender justice movements in all their diversity. It is a transformative space created by and for the movements - where Global South feminists and historically marginalized communities take centerstage, strategize to shift power, and connect with allied movements, funders and policy-makers. And so it is with full and fiery hearts that we share…
The 15th AWID International Forum will take place from December 2-5, 2024 in Bangkok, Thailand!
We hope to gather 2,500 in-person and 3,000 online/hybrid participants. When thousands of feminists come together, we create a sweeping force of solidarity that has the power to change the world! We’re excited, and we know you’re excited too - so stay tuned for more

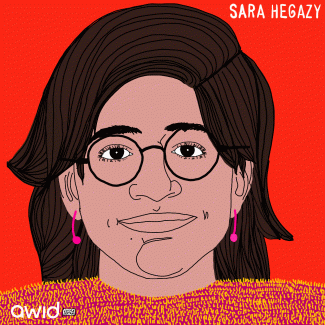
Sara Hegazy, une audacieuse activiste égyptienne des droits des LGBTQI+, vivait dans une société où les membres de sa communauté, leurs corps et leurs vies sont souvent victimes de préjugés mortels. La résistance de Sara puise ses racines dans le processus de déconstruction d'un système dominant, oppressif et patriarcal, et de ses acteurs antidroits.
« [En Égypte], toute personne qui n'est pas un homme, musulman, sunnite, hétéro et partisan du système, est rejetée, réprimée, stigmatisée, arrêtée, exilée ou tuée. Ce phénomène concerne le système patriarcal dans son ensemble, étant donné que l'État ne peut pratiquer sa répression contre les citoyens sans une oppression préexistant depuis l'enfance », écrivait Sara Hegazy le 6 mars 2020
La répression de la voix de Sara par le gouvernement égyptien atteignit son paroxysme en 2017, lorsqu’elle fut arrêtée pour avoir brandi un drapeau arc-en-ciel lors du concert de Mashrou' Leila (groupe libanais dont le chanteur principal est ouvertement gai) au Caire. Elle fut ensuite accusée d'avoir rejoint un groupe illégal et « d’incitation à la déviance sexuelle et à la débauche ».
« C’était un acte de soutien et de solidarité, non seulement envers le chanteur [de Mashrou' Leila] mais pour tou·te·s les opprimé·e·s… Nous étions fier·ère·s de porter le drapeau. Nous ne pouvions imaginer que la société et l’État égyptien réagiraient de cette façon. Ils m’ont vue comme une criminelle, quelqu’un qui cherchait à détruire la structure morale de la société ». - Sara Hegazy
Sara fut emprisonnée pendant trois mois, durant lesquels elle fut torturée et agressée sexuellement. En janvier 2018, après avoir été libérée sous caution, elle demanda l'asile au Canada où elle vécut en sécurité mais resta prisonnière des souvenirs de la violence et des sévices qu'elle avait subis dans son corps et son âme.
« Je suis sortie de cette expérience au bout de trois mois avec un cas très sévère et grave de SSPT [syndrome de stress post-traumatique]. La prison m'a tuée. Elle m'a détruite », déclara Sara Hegazy à la NPR (Radio d’État)
Sara s'est suicidée le 14 juin 2020, en laissant une note manuscrite en arabe :
« À mes frères et sœurs - j'ai essayé de trouver la rédemption et j'ai échoué, pardonnez-moi. »
« À mes amis - l'expérience [l’aventure] a été rude et je suis trop faible pour la supporter, pardonnez-moi. »
« Au monde - tu as été très cruel, mais je te pardonne. »
Son courage et son héritage seront perpétués par toutes les personnes qui l’aimaient et qui croient en ce pour quoi elle s’est battue.
« À Sara : repose-toi, repose-toi simplement, hors d’atteinte de cette violence implacable, de ce patriarcat étatique meurtrier. Dans la rage, dans le chagrin, dans l'épuisement, nous résisterons. » - Rasha Younes, chercheuse sur les droits LGBT à Human Rights Watch. Lisez le texte complet
Le chanteur de Mashrou’ Leila chante en hommage à Sara Hegazy

Cuando miles de feministas se unen, creamos una fuerza arrolladora de solidaridad que tiene el poder de cambiar el mundo. El Foro de AWID será un momento para que descansemos y nos recuperemos juntas, nos conectemos más allá de las fronteras y descubramos nuevas y osadas direcciones estratégicas.
La fecha y el lugar se anunciarán el próximo año, tan pronto como podamos. Estamos emocionades y sabemos que ustedes también lo están. ¡Manténganse al tanto!
¡Asegúrate de seguirnos en las redes sociales y suscríbete a nuestra lista de correo para mantenerte al día!
Ya puedes mirar el programa «Feminist Embodiments of Hope and Power» [«Corporizaciones feministas de esperanza y poder»] del Club de Cine Feminista de AWID, una serie de películas sobre realidades feministas de la región del Sudoeste Asiático y África del Norte, curada por Esra Ozban.